Minimally-Invasive Procedures for Valvular Disease Treatment

Vascular heart disease affects over 8 million people in the United States, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Vascular disease treatment has traditionally been associated with open-heart surgery to repair or replace the affected heart valve, which can cause health complications and lead to extensive hospital stays and recovery time. Additionally, only some people with valvular disease are candidates for valve repair or replacement options due to certain risk factors. Fortunately, recent medical breakthroughs have led to less invasive treatment options.
Medication
The least invasive valvular disease treatment is medication. While medication cannot cure valvular heart disease, it can relieve swelling, abnormal heart rhythm, high blood pressure, and other common symptoms. The cardiologist may prescribe the following medication:
- Diuretics. Also known as water pills, this medication reduces swelling and fluid buildup in the tissues and bloodstream.
- Blood thinners. Blood thinners can prevent blood clots and decrease the risk of other cardiac issues.
- Antiarrhythmics. These medications prevent and treat abnormal heartbeats or arrhythmias.
If the patient has another heart condition in addition to valvular heart disease (i.e., coronary heart disease), the cardiologist may prescribe medications that can help reduce the workload on the heart and relieve their symptoms.
Minimally invasive surgery
A diseased or damaged heart valve may eventually need to be repaired or replaced, even if the patient exhibits no symptoms. Untreated valve disease can lead to decreased heart function, limiting future treatment options for the patient. The cardiologist tailors treatment to the patient's valvular disease and its location, considering the patient's age, general health, and other lifestyle factors.
Valvuloplasty
Also known as balloon valvuloplasty, this minimally invasive valvular disease treatment addresses valvular stenosis, where a heart valve narrows and hinders the smooth flow of blood. During this procedure, the cardiologist guides a balloon-tipped catheter through a vein in the patient's arm or groin. Once it reaches the damaged valve, the balloon is inflated to widen it. This allows for improved blood flow and reduces strain on the heart. It is particularly effective in treating aortic and pulmonary valve stenosis.
Annuloplasty
An annuloplasty aims to repair the valve's annulus—the outer ring-like structure that supports the valve. This technique can help treat mitral valve regurgitation and mitral valve stenosis. Making a small incision in the patient's rib cage, the cardiologist can tighten a leaky mitral valve by placing a mesh or metal ring around it. Researchers are currently studying less invasive ways to perform annuloplasty through transcatheter procedures.
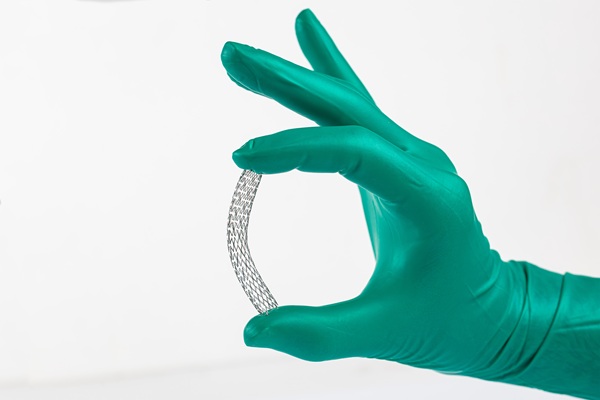
Transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR)
Also known as transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI), TAVR is an effective, minimally invasive procedure for patients with severe aortic stenosis who need a valve replacement. Similar to placing a stent inside an artery, the cardiologist threads a catheter through an artery to the damaged or diseased valve. They then place the new valve inside the old valve. Some implanted valves are "spring-loaded" and can expand on their own, while others need to be expanded using a balloon. Once the new valve expands, it moves the old valve out of the way, taking over the duty of regulating blood flow.
There are many approaches that a cardiologist can use to safely and effectively access the damaged valve. The two most common are transfemoral and transapical.
Transfemoral
This technique is where the cardiologist enters through the femoral artery — a large artery in the groin — so they do not need to make an incision in the patient's chest.
Transapical
The cardiologist makes a small incision in the chest and enters the heart through the apex, the tip of the left ventricle.
Transcatheter edge-to-edge repair (TEER)
For patients with mitral regurgitation, the cardiologist can access the mitral valve with a catheter through a vein in the patient's leg. They attach a small chip to the mitral valve to help close it. The TEER technique helps restore regular blood flow through the heart.
Schedule an appointment today
The goal of the team at Florida Premier Cardiology is to provide our patients with the best and safest treatments. We tailor your treatment to your unique situation and health. Every heart is different; your valvular disease treatment should be, too. Call our office to schedule an appointment today.
Request an appointment here: https://boyntonbeach.floridapremiercardio.com or call Florida Premier Cardiology at (561) 229-1411 for an appointment in our Boynton Beach office.
Check out what others are saying about our services on Yelp: Valvular Disease Treatment in Boynton Beach, FL.
Recent Posts
Coronary stent placement is a treatment for coronary artery disease, a buildup of plaque (fat and cholesterol) around the heart's arteries. Along with angioplasty, a stent helps restore blood flow to the heart, relieving symptoms such as chest pain and shortness of breath and helping prevent a heart attack. The following overview of coronary stent…
Heart disease treatment encompasses a range of interventions, from lifestyle changes and medications to surgical interventions. Individuals can manage their condition and improve their quality of life by working with a cardiologist. Successful heart disease treatment starts with the patient having the information they need to make informed decisions about their health.Also known as cardiovascular…
A heart specialist is a doctor specializing in diagnosing and treating cardiovascular conditions. Patients may be referred to one of these doctors for several reasons, from diagnosing a heart health issue to getting cleared for surgery. However, seeing a heart specialist is even more crucial for those either experiencing the signs of heart disease or…
Cardiologists perform angioplasty to open blocked arteries, specifically those caused by coronary disease. This minimally invasive alternative to open heart surgery can restore proper blood flow to the heart and often reverse the fast track to a heart attack. However, learning when one is necessary is crucial for treatment success.Coronary artery disease (CAD) is a…