Types of Echocardiograms
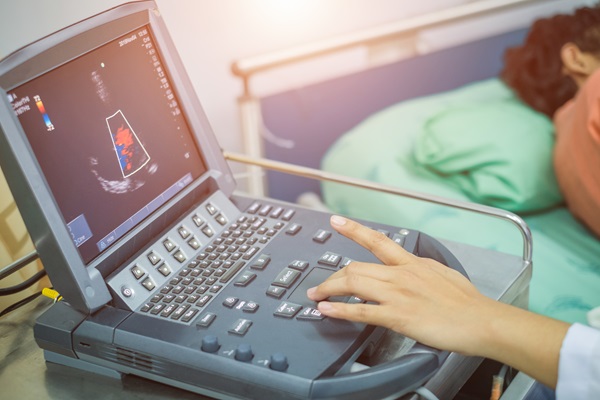

Echocardiograms use ultrasounds, or sound waves, to quickly and efficiently get information about your heart. A cardiologist uses an echocardiogram when they have questions or concerns about the size, shape, and performance of your heart and its structures, such as the valves and chambers. This minimally invasive procedure can help cardiologists identify and diagnose various cardiac conditions.
Types of echocardiograms
Transthoracic echocardiogram (TTE)
The most common type of echocardiogram is a transthoracic echocardiogram (TTE). This procedure involves a cardiologist placing a transducer on the chest, using ultrasound (sound waves) to create images of a patient's heart. TTEs help providers see the patient's heart, its four chambers and valves, and nearby blood vessels. It can determine how well the heart is pumping blood and how quickly blood flows through it.
A cardiologist may use TTE to identify causes of cardiac-related symptoms, such as chest pain, swelling (edema), heart murmurs, and shortness of breath (dyspnea). They can also use TTE to screen, diagnose, or follow up on medical conditions. These medical conditions may include:
- Aortic aneurysm or dissection
- Blood clots
- Heart failure
- Heart valve disease
- Sudden changes in electrocardiogram (ECG) results
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- Tumors (cardiac cancer)
TTEs are painless and noninvasive. Patients do not need any special preparation before undergoing this test and will not have to set aside recovery time.
During a TTE, the patient will remove their clothes from the waist up and put on a gown before lying on their back or side on a medical table. If the cardiologist needs to use a contrast dye or saline solution, they inject or infuse it. Then, they will apply gel to the patient's chest and move the wand across it to collect images. The cardiologist may ask the patient to change position or hold their breath for short intervals.
Transesophageal echocardiogram (TEE)
If the cardiologist needs more detailed images of the patient's heart, they may choose to perform a transesophageal echocardiogram (TEE). This procedure involves inserting a specialized transducer down the patient's throat and esophagus to get clearer and closer images of the heart. The transducer then sends these echoes to a computer that turns them into images. TEE is particularly useful for assessing cardiac structures that are difficult to visualize with a TTE, such as the posterior heart valves or the atria. They can also help provide real-time imaging during or after undergoing a catheter-based procedure.
A transesophageal echocardiogram can help diagnose and manage different heart conditions. These may include:
- Aortic aneurysm
- Atrial fibrillation
- Cardiac tumors
- Congenital heart disease
- Heart valve disease
- Infective endocarditis
- Pericardial disease
A TEE is more invasive than a TTE since the provider needs to insert a device inside the patient's body. The provider will spray the back of the patient's throat with a pain-relieving medication and give them an IV to mildly sedate them and reduce discomfort during the procedure. However, some patients may need general anesthesia to be fully asleep, and the cardiologist will need to place them on a breathing machine; using general anesthesia will make a recovery longer than if they were mildly sedated. TTEs typically take up to 90 minutes.
Exercise stress echocardiogram
An exercise stress echocardiogram is where the cardiologist takes an ultrasound of the patient's heart before and after exercise. It produces moving images showing how well their heart functions under stress, typically after exercising on a treadmill or stationary bike. This test is also known as a stress echo or echo stress test.
The cardiologist most often orders an exercise stress echocardiogram to diagnose an individual with coronary artery disease. This condition is where the blood vessels that carry blood to the heart muscle are blocked. Stress echos can also help diagnose or monitor conditions such as cardiomyopathy, heart failure, and pulmonary hypertension.
An echocardiogram is an essential tool to protect your heart health
An echocardiogram is an important test that reveals crucial information about your heart's structure and function. While the process varies from test to test, they are typically minimally invasive and painless. If your healthcare provider has recommended an echocardiogram, call our office to learn more or schedule a consultation.
Request an appointment here: https://boyntonbeach.floridapremiercardio.com or call Florida Premier Cardiology at (561) 229-1411 for an appointment in our Boynton Beach office.
Check out what others are saying about our services on Yelp: Echocardiograms in Boynton Beach, FL.
Recent Posts
Coronary stent placement is a treatment for coronary artery disease, a buildup of plaque (fat and cholesterol) around the heart's arteries. Along with angioplasty, a stent helps restore blood flow to the heart, relieving symptoms such as chest pain and shortness of breath and helping prevent a heart attack. The following overview of coronary stent…
Heart disease treatment encompasses a range of interventions, from lifestyle changes and medications to surgical interventions. Individuals can manage their condition and improve their quality of life by working with a cardiologist. Successful heart disease treatment starts with the patient having the information they need to make informed decisions about their health.Also known as cardiovascular…
A heart specialist is a doctor specializing in diagnosing and treating cardiovascular conditions. Patients may be referred to one of these doctors for several reasons, from diagnosing a heart health issue to getting cleared for surgery. However, seeing a heart specialist is even more crucial for those either experiencing the signs of heart disease or…
Cardiologists perform angioplasty to open blocked arteries, specifically those caused by coronary disease. This minimally invasive alternative to open heart surgery can restore proper blood flow to the heart and often reverse the fast track to a heart attack. However, learning when one is necessary is crucial for treatment success.Coronary artery disease (CAD) is a…